Is H2s Polar
Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless, flammable gas infamous for its foul odor reminiscent of rotten eggs. While its smell might be off-putting, the molecule itself holds significant interest in scientific circles due to its unique properties, including its polar nature. In this article, we delve into the molecular structure of H2S to uncover whether it exhibits polarity and explore the implications of its polarity in various contexts.
Understanding Polarity
Polarity in molecules arises due to differences in electronegativity between atoms, causing an uneven distribution of electron density. This imbalance creates a partial positive charge on one end of the molecule and a partial negative charge on the other. Polar molecules, such as water (H2O), exhibit this characteristic, leading to various intriguing phenomena like hydrogen bonding and solubility.
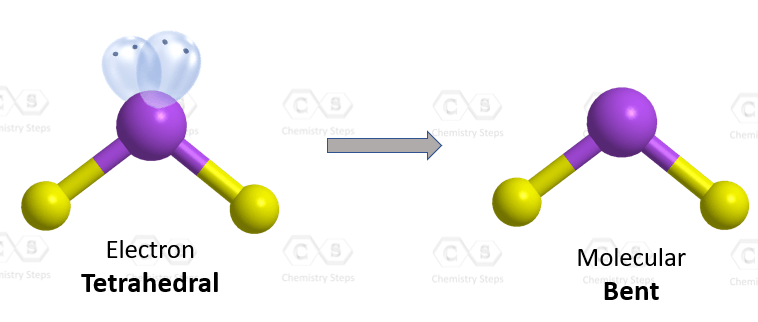
Molecular Structure of H2S
H2S consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to a sulfur atom via covalent bonds. Sulfur is less electronegative than oxygen, the atom it is often compared to due to their position in the same group on the periodic table. However, sulfur is still more electronegative than hydrogen. As a result, the sulfur atom in H2S pulls electron density towards itself, generating a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen atoms acquire partial positive charges. This distribution suggests that H2S should exhibit polarity.
Experimental Evidence
Experimental studies utilizing various techniques, including infrared spectroscopy and dipole moment measurements, support the polar nature of H2S. Infrared spectroscopy reveals characteristic absorbance peaks associated with asymmetric stretching vibrations of the H-S bonds, indicating the presence of an uneven distribution of electron density. Dipole moment measurements further confirm the molecule’s polarity, with the dipole moment of H2S being non-zero.
Implications of Polarity
The polarity of H2S has profound implications in different fields. In biology, H2S is recognized for its role as a signaling molecule, akin to nitric oxide and carbon monoxide. Its polar nature allows it to interact with polar regions of biomolecules, influencing various physiological processes such as vasodilation and inflammation. Moreover, understanding the polarity of H2S is crucial in environmental studies, especially concerning its behavior in aqueous environments and its impact on atmospheric chemistry.
Conclusion
Hydrogen sulfide exhibits polarity due to differences in electronegativity between sulfur and hydrogen atoms. This polarity is evidenced by experimental techniques and has significant implications in diverse fields ranging from biology to environmental science. Further exploration of H2S’s polar nature promises to unravel additional insights into its properties and applications, fueling ongoing research interest in this intriguing molecule.






